Meniscus Surgery: Cost, Recovery & Success Rates
You heard a pop in your knee while playing football or lifting a heavy weight. After some time, your knee started locking up when you bent. Swelling and pain began to increase day by day. You've rested, you've tried stretching, but nothing has been found effective.
Meniscus surgery might be the solution for your problem. Continue reading to know when surgery makes sense, what each procedure involves, and how to plan for costs and recovery.
What is a meniscus and meniscus surgery?
Our knee joint has two menisci. Each meniscus is a C-shaped or crescent-shaped fibrocartilage pad present between the thigh bone (femur) and shin bone (tibia). These menisci serve as both a cushion and a stabilizer, helping our knee move smoothly while maintaining stability.
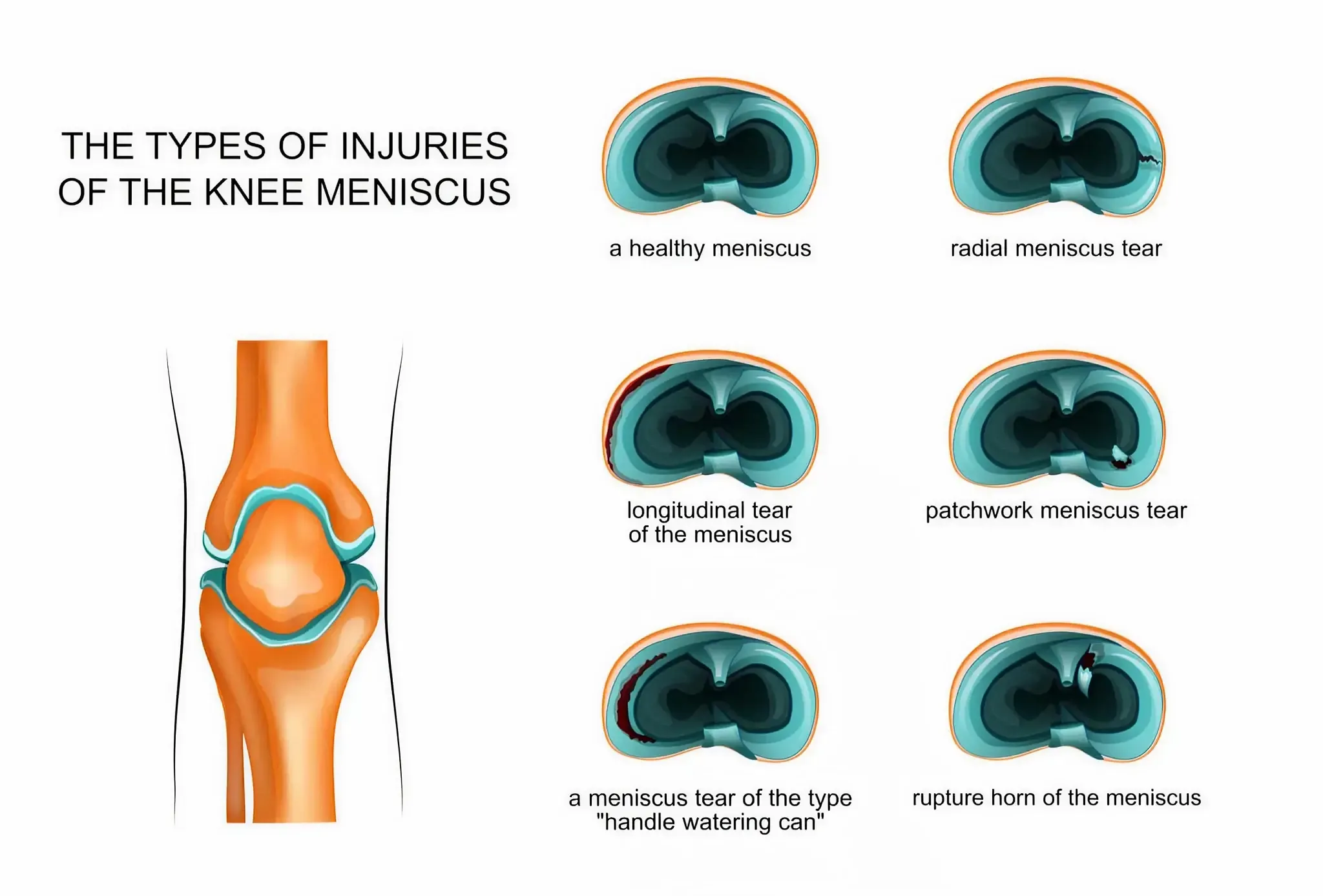
Meniscus tear and its causes
Although menisci provide stability to your joint, they are also highly prone to tears. Meniscus tear is one of the most common knee injuries, especially in athletes and older individuals.
You may feel pain, swelling, stiffness, or trouble while straightening the knee. Some of the common causes leading to a meniscus tear are:
-
Sudden twisting movement
-
Squatting or lifting heavy weights
-
Aging and wear and tear of menisci
-
Obesity and excess weight
-
Genetic and anatomical features of menisci
What is meniscus surgery?
Meniscus surgery is a medical procedure that surgeons use to treat a torn or damaged meniscus. It is usually performed by arthroscopy, which involves inserting a small instrument and camera through tiny incisions in the knee joint.
In the torn meniscus surgery, either your doctor repairs a torn meniscus or removes the damaged part.

When is meniscus surgery recommended?
Not every meniscus tear needs surgery. In many cases, non-surgical treatment options like physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medicines, and rest are enough to promote healing. But when these options don’t work, surgery may be the only way to fix the torn meniscus.
Here are some things your doctor might consider before recommending you a surgery:
-
When therapy fails: Your doctor can choose the surgical method when the non-surgical treatment becomes less effective in healing the torn meniscus.
-
Tear type and location of meniscus: The outer third of the menisci (“red zone”) has a good blood supply, which helps heal the tears on their own. But the inner two-thirds (“white zone”) of the cartilage has a poor blood supply, which slows down the healing process of tears. So, these white zone tears usually require surgical interventions.
-
Age considerations: Although meniscus surgery has less strict age limits, younger people (below 40) heal better after meniscus surgery. So, if you are younger and physically active, your doctor may opt for surgery.
Usually, your doctor can recommend surgery when your torn meniscus causes persistent pain, knee instability, or locking, especially when the non-surgical treatment fails.
Considering meniscus surgery? QCG can help you find top orthopedic surgeons worldwide — hassle-free and affordable. Contact us now!
Types of meniscus surgery procedures
Once your doctor decides surgery is the best option, the next step is choosing the right procedure. That depends on where and how badly your meniscus is torn.
1- Meniscus repair
In this method, your surgeon stitches the torn edges of your meniscus back together using arthroscopy. This procedure preserves the cartilage, helps maintain the normal knee function, and reduces the risks of long-term arthritis (inflammation of the joint).
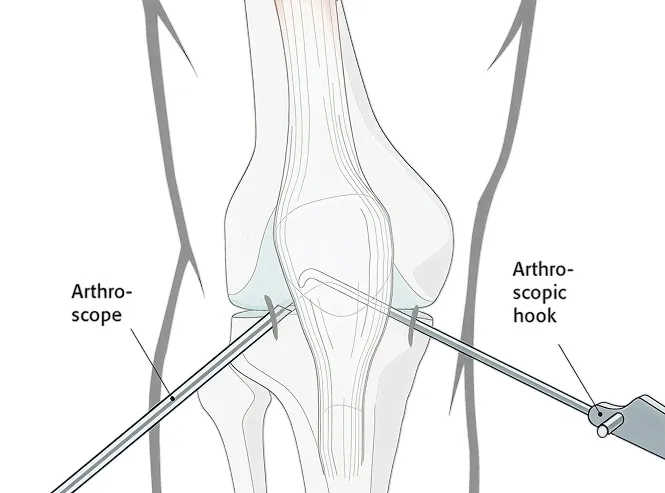
This surgery works best when:
-
The tear is in the “red zone” (having a good blood supply) of the cartilage.
-
You are young and physically active.
-
You don’t have advanced arthritis.
Although it has a high success rate, it does come with some downsides, like a longer recovery time, needing crutches, and wearing a knee brace for several weeks.
2- Partial meniscectomy
It is a common knee surgery in which your surgeon removes the torn or damaged part of the meniscus, leaving back the healthy part. Doctors usually recommend it when the tear is in a part of the meniscus that doesn’t get enough blood flow to heal naturally.
It is a minimally invasive method with a short recovery period. This surgery normally restores the knee's function. Studies suggest up to 90% of patients report satisfaction after arthroscopic partial meniscectomy, significantly more than after open total removal.
While this option can provide quick relief, it reduces the cushioning in your knee, resulting in increased joint stress. Over time, this added pressure wears down the cartilage and raises the risk of developing knee arthritis.
3- Total meniscectomy
Total meniscectomy involves the removal of the entire meniscus when the meniscus is completely damaged. Your orthopedic surgeon may recommend this option if the tear is too large or complex to heal on its own. It’s especially considered when the damage is related to age-related degeneration or if previous treatments haven’t worked.
Total meniscectomy can relieve pain and improve mobility when other treatments don’t work. The removal of the meniscus in this procedure decreases the cushioning effect in the knee, which leads to increased joint stress. Over time, cartilage of the knee joint wears off, resulting in increased osteoarthritis (Inflammation of the bone and joint) risk.
Older studies claim that only about two-thirds of patients had good outcomes even 10–30 years after surgery. Surgeons now choose partial meniscectomy over total removal, unless necessary.
4- Meniscus transplant
Meniscus transplant or meniscus allograft transplantation is a surgical procedure in which the doctors replace the damaged or missing meniscus with a donor’s healthy meniscus.
A meniscus transplant is typically recommended for individuals who:
-
Have previously undergone a meniscectomy
-
Have a severely damaged or missing meniscus that cannot be repaired.
-
Are athletes or physically active
-
Are below the age of 50
Research indicates that around 73% of meniscus transplants remain functional at 10 years, and about 60% last up to 15 years.
Meniscus transplantation is a complex procedure typically performed at specialized medical centers. While it is generally safe, potential risks include infection, incomplete healing, and graft rejection.
Preparing for meniscus surgery
Getting ready for meniscus surgery helps make the procedure safer and your recovery smoother.
Here’s what you can expect:
Preoperative preparation
Before surgery, you need to follow some specific instructions.
-
Your doctor assesses your overall health to determine your fitness for surgery. This usually includes blood tests, an ECG, a chest X-ray, and advanced imaging like an MRI.
-
Inform your doctor about the medications and supplements you are currently taking. Stop taking blood thinners and NSAIDs beforehand.
-
If you are a smoker or obese, try to quit smoking and lose weight to improve healing.
-
In some cases, your doctor may prescribe specific prehab exercises to strengthen your knee before surgery.
-
Shower with antiseptic soap the night before to lower the risk of infection.
-
Nothing to eat or drink for 12 hours before surgery.
Step-by-step surgical process
Here is what happens during meniscus surgery:
-
Your surgeon will give you anesthesia to make you unconscious.
-
Two to three small incisions of about half an inch each are made around your knee.
-
Through one incision, a tiny specialized camera (arthroscope) is inserted to view inside the knee.
-
Other incisions allow the doctor to put instruments in.
-
A surgeon generally inspects the tear and other knee structures through the arthroscope and decides the appropriate surgical intervention based on the evaluation.
For meniscus repair: The torn meniscus is stitched together using sutures or small anchors.
For partial meniscectomy: Small shavers or scissors are inserted inside the knee through the small incisions. These scissors trim away the torn fragment of the meniscus.
For meniscus transplant: The damaged meniscus is removed, and the donor’s healthy graft is fixed in place.
- Incisions are then closed with stitches or steri-strips, and sterile dressings are applied to the incision sites.
How long is the recovery from meniscus repair?
On average, full recovery from meniscus surgery can take 6 to 9 months, but it depends on your age, tear type, and how well you follow post-op instructions.
Days 0-14
-
You can go home the same day in most cases.
-
Early range of motion exercises begin under the guidance of a physical therapist.
-
Crutches or a knee brace are usually needed to keep weight off the joint.
First 2-6 weeks: Healing phase
-
Continue using crutches and the knee brace
-
Focus on the gentle bending of the knee.
6-12 weeks: Rehab and strengthening
-
Braces usually come off by 6 or 8 weeks after surgery.
-
You'll begin a full range of exercises to strengthen your leg muscles.
3 to 6 Months: Return to normal activities
-
You may slowly return to walking without a limp, climbing stairs, and light jogging.
-
Athletes can expect 6 months or longer before returning to full sport-level performance.
Recovery is just as important as the surgery itself. With QCG, get connected to clinics offering excellent post-surgery rehab programs worldwide.
Start your journey to a pain-free knee today!
Risks and complications of meniscus surgery
Surgery for a meniscus tear is generally safe and effective, but it carries some risks and potential long-term side effects.
Common risks
Like all surgeries, meniscus surgery also has certain immediate risks.
-
Infection: Infections are rare in meniscus surgery, but can occur at the incision site.
-
Blood clots: Deep vein thrombosis (blood clot formation in a deep vein) is a potential risk, especially if mobility is limited after surgery.
-
Nerve or blood vessel damage: There is a slight chance of injury to surrounding nerves or blood vessels during the procedure.
-
Anesthesia complications: Reactions to anesthesia, including nausea or dizziness, may occur.
Long-term side effects
Some patients may experience long-term problems after surgery for a meniscus tear.
-
Osteoarthritis: Removing all or part of the meniscus can cause osteoarthritis (a condition where your bones become fragile).
-
Re-injury: A repaired meniscus can again become susceptible to tear, especially if you are subjected to high-impact activities before the full recovery.
-
Persistent knee pain & stiffness: Even after the successful surgery, you may experience ongoing pain and stiffness in your knee.
What is the success rate of meniscus repair?
Overall, meniscus repair has good success rates, with only a few people experiencing failures. A 2022 review found that roughly 19–20% of repairs had failed by 5–7 years, implying about an 80–81% success rate.
Success rate is usually higher for tears in the vascular (red) zone and when performed soon after injury. In cases when a repair fails, a second surgery (often a partial meniscectomy) can be done. Importantly, clinical success (patients feeling better and returning to activities) is often higher in the short term. Many people report good outcomes at 1–2 years.
How much does meniscus surgery cost?
The cost of meniscus surgery varies depending on the country, hospital, and procedure type. On average, meniscus repair surgeries can range from $2,000 to $15,000 worldwide.
Here’s a quick look at how meniscus surgery costs stack up around the world:
| Country | Cost Range (USD) |
|---|---|
| USA | $9,000 – $12,000 |
| UK | $5,000 – $16,000 |
| India | $2,000 – $6,000 |
| Thailand | $3,500 – $6,500 |
| Turkey | $2,200 – $7,500 |
| Mexico | $2,500 – $12,000 |
| Singapore | $4,000 – $7,000 |
| Germany | $3,300 – $6,600 |
| South Korea | $3,500 – $7,000 |
| Poland | $3,700 |
Note: The above costs are estimates. The original cost may vary depending on the clinic and the surgeon’s experience.
Factors influencing the cost of meniscus repair surgery
The price of meniscus repair varies in different countries, even in different hospitals and cities of the same country. Here are some common factors that could influence the cost:
-
Complexity of the tear: Simple tears require less extensive procedures, while complex and degenerative tears need more involved surgeries, leading to increased expenditures.
-
Use of grafts: Use of implants adds to the overall expenses of surgery.
-
Hospital and surgeon factors: Private hospitals charge more for meniscus repair than public hospitals. Highly experienced surgeons have higher fees.
-
Location: The cost of surgery also depends on where you get it. You could find more affordable prices in India, Turkey, and Poland than in the U.K. or the U.S.
-
Additional medical expenses: Expenses of consultation, imaging, physical therapy, and post-surgery medications can influence the total cost of surgery.
Want to know exactly what meniscus surgery will cost you? Ask QCG for a customized quote now.
Is meniscus surgery covered by insurance?
Yes, in many countries, meniscus surgery is covered by health insurance when it's considered medically necessary. For example, in the US, most insurance plans, like Medicare and most private insurers, cover meniscus surgery.
Even with insurance, you may have to pay certain expenses, including deductibles, copayments & coinsurance, and non-covered services. For example, in the U.S., out-of-pocket costs for arthroscopic knee surgery can range from $2,700 to $3,200, depending on the insurance plan.
In countries with a universal health system (Canada, UK, EU, etc.), the surgery is generally covered by general tax revenues or national resources.
Is a meniscus surgery worth it?
In most cases—yes, it’s absolutely worth it.
If your knee pain won’t quit and other treatments haven’t worked, surgery can bring relief. It’s a common and safe procedure that helps lots of people get back to work, exercise, or simply move around without pain.
But remember, it’s not the same for everyone. Your age, activity level, and the kind of tear you have all play a role. With proper care and rehab, though, meniscus surgery can be the key to stronger knees and a more comfortable, active life.
And if you’re thinking about surgery, why not explore affordable, quality options abroad? QCG (Quality Care Global) makes it easy to find top surgeons and hospitals worldwide. Get in touch today!