Sleep Apnea: Signs, Causes, and Treatment Options for Better Sleep
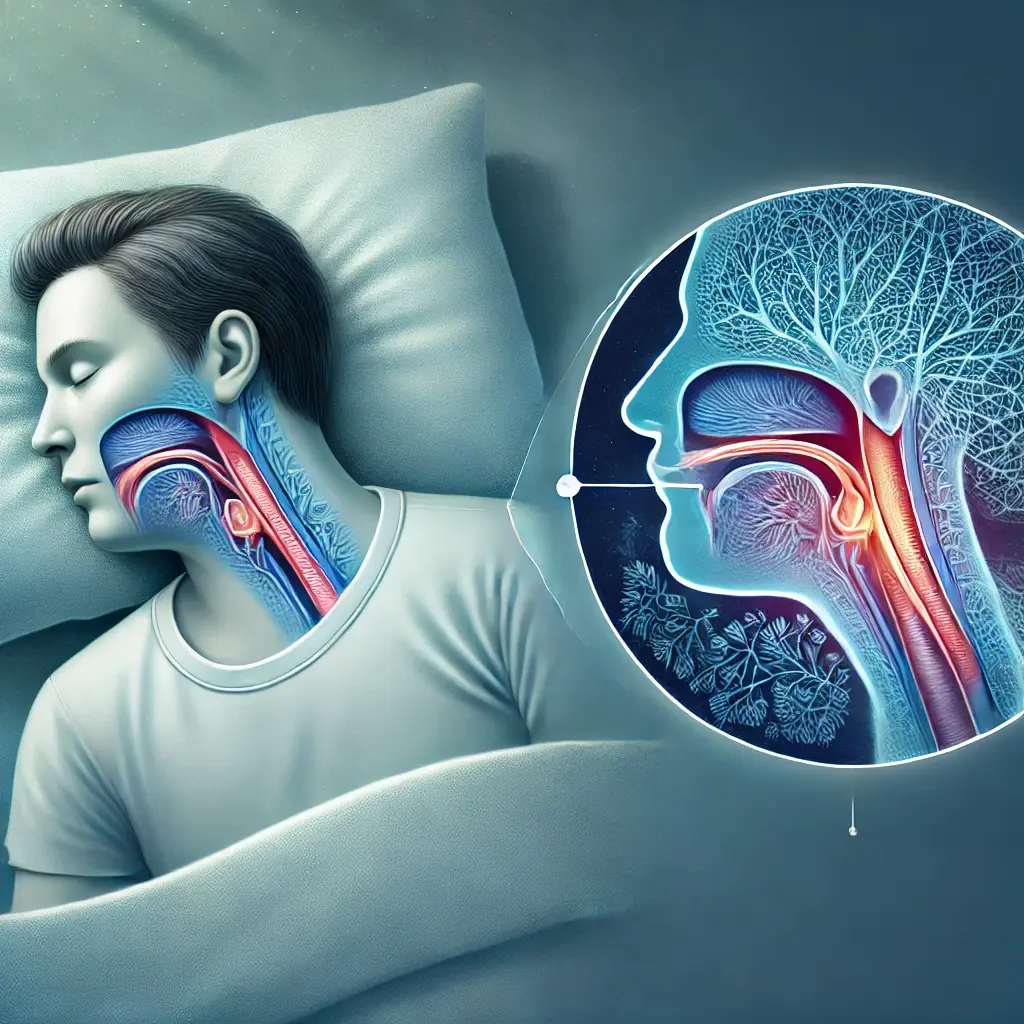
Are you waking up exhausted, even after a full night’s sleep? Does your partner nudge you awake because your snoring sounds like a chainsaw? If so, you might have sleep apnea.
This common but serious sleep disorder can disrupt your nights and impact your health if left untreated. It could lead to serious issues like high blood pressure and diabetes.
But don’t worry! sleep apnea is manageable. And there are several treatment options available. Let’s explore what sleep apnea is and how you can find the right treatment:
What is sleep apnea?
Imagine your breathing stops and starts repeatedly while you’re asleep. That’s what happens in sleep apnea.
The word apnea comes from a Greek word meaning “breathless”. Since you have difficulty breathing during sleep, it is known as sleep apnea.
These frequent pauses during sleep can last from a few seconds to a minute. As a result, they disrupt your sleep and prevent you from getting quality sleep.
Sleep apnea varies in severity:
- Mild cases involve 5 to 15 breathing interruptions per hour.
- Moderate cases see 15 to 30 episodes in one hour.
- Severe cases occur when the interruptions happen 30 or more times per hour.
No matter the severity, untreated sleep apnea can have serious implications for your health.
Types of sleep apnea
There are three types of sleep apnea, including:
1. Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
This is the most common type of sleep apnea. In this condition, your airway gets blocked while you sleep, usually because the muscles in your throat relax too much. This causes pauses in breathing, which can disrupt your sleep and affect your overall health.
Before the age of 50, OSA is prevalent in men while after 50, it’s common in women. Also, the likelihood of developing OSA increases with age.
2. Central sleep apnea (CSA)
In CSA, the problem isn’t a blocked airway. Instead, your brain doesn’t send the proper signals to your breathing muscles. Even though your airway remains open, your body doesn’t try to breathe for a short period. It is more common in people over 60 years.
3. Complex sleep apnea syndrome (Mixed apnea)
This is a combination of both types. It typically starts as OSA, but after starting treatment, CSA symptoms may also appear. This makes it difficult to treat.
Warning signs of sleep apnea
Not sure if you have sleep apnea? Here are some signs to watch for:
- Loud snoring
- Restless sleep
- Night sweats
- Gasping or choking sounds
- Stopped breathing during sleep
- Dry mouth or sore throat in the morning
- Feeling very sleepy during the day
- Mood changes or irritability
- Trouble concentrating
- Morning headaches
Other signs include:
- Low sex drive
- High blood pressure
- Frequent urge to go to bathroom at night
In children, look for:
- Heartburn
- Bedwetting
- Night sweats
- Hyperactivity
- Poor school performance
- Unusual sleeping positions
- Moving legs or arms while sleeping
Do any of these sound familiar? If so, don’t ignore it. Sleep apnea can have long-term effects. But the sooner you address it, the better.
Causes of sleep apnea
There could be several causes of sleep apnea, depending on its type. Let’s have a look:
Causes of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
OSA can occur due to:
- Muscle relaxation: Throat muscles relax excessively during sleep, blocking the airway.
- Anatomical factors: Enlarged tonsils, adenoids, or a large tongue can obstruct airflow.
- Obesity: Extra weight increases the likelihood of airway collapse.
- Neuromuscular conditions: Conditions like stroke affect brain signals to breathing muscles.
- Endocrine disorders: Hormonal issues such as hypothyroidism can contribute to OSA.
Causes of central sleep apnea (CSA)
On the flip side, the causes of CSA are:
- Brain signaling issues: The brain fails to send proper signals to control breathing muscles.
- Heart failure: Associated with Cheyne-Stokes breathing patterns.
- **Neurologic disorders:**Conditions affecting the brainstem can disrupt breathing control.
- Idiopathic forms: Some cases have unknown causes.
- High-altitude: People living at higher altitudes might get CSA.
Risk factors of sleep apnea
Depending on the cause, several factors can increase your risk of developing sleep apnea. Let’s take a closer look!
What are the risk factors for OSA?
Several things can raise your chances of having obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Here are some key factors to watch for:
- Extra weight: Carrying extra pounds, especially around your neck, can block your airway during sleep.
- Thick neck: A thicker neck might mean a narrower airway, which can lead to OSA.
- Narrow airway: Some people are born with narrow airways, and enlarged tonsils or adenoids can make it worse.
- Gender and age: Men are more likely to get OSA, and the risk increases as you get older.
- Family history: If sleep apnea runs in your family, your risk is higher.
- Substance use: Alcohol, sedatives, and tranquilizers relax your throat muscles, making you more susceptible to OSA.
- Smoking: Smoking irritates your airway and raises the risk.
- Nasal issues: Trouble breathing through your nose due to congestion or allergies can increase your chances.
- Health conditions: Things like high blood pressure, diabetes, and heart disease can also put you at higher risk.
What are the risk factors for CSA?
Central sleep apnea (CSA) has its own unique risk factors. Here’s what to look out for: Age: The risk of CSA is higher in middle-aged and older adults. Gender: Men are more likely to have CSA than women. Heart issues: Conditions like heart failure can raise your risk. Opioid use: Long-acting opioids can interfere with your normal breathing patterns, increasing the risk of CSA. Stroke: Having a stroke increases the chances of developing CSA. Neurological conditions: Problems that affect the brain, like ALS (Lou Gehrig's disease), can interfere with your breathing control.
Keep an eye on these risk factors, especially if you have more than one. The earlier you catch it, the better!
Treatment options for sleep apnea
There are several ways to treat sleep apnea depending on how severe it is and what’s causing it. Here’s a look at the main options:
Lifestyle changes
For mild cases, simple lifestyle adjustments can make a big difference:
- Lose weight if you're overweight.
- Reduce alcohol consumption and avoid it close to bedtime.
- Quit smoking, which can worsen apnea.
- Change your sleep position—sleeping on your side can improve airflow.
CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure)
CPAP is the most common treatment used for moderate to severe sleep apnea. It provides a steady flow of air through a mask to keep your airway open while you sleep.
Though it might take some time to get used to, many users feel more alert and sleep better after just a few nights.
BPAP (Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure)
Similar to CPAP, it offers two levels of air pressure—higher when you inhale and lower when you exhale. This can make it more comfortable for some people, especially those who find it challenging to exhale against continuous pressure.
APAP (Auto-Adjusting Positive Airway Pressure)
APAP machines automatically modify the air pressure during the night based on your breathing patterns. This adaptability makes APAP more versatile than CPAP or BPAP, as it provides a custom air pressure level designed to meet your specific needs.
Oral appliances
If the idea of a CPAP machine doesn’t appeal to you, a dentist can fit you with a custom mouthpiece that adjusts your jaw and keeps your airway open.
Medications
While there isn’t a specific medication to cure sleep apnea, some drugs can help with related issues.
For example, medications may be prescribed to relieve nasal congestion or to improve daytime alertness. These can enhance your overall comfort and make it easier to manage sleep apnea symptoms.
Surgery
In severe cases, surgery might be needed. This could involve removing extra tissue from your throat or fixing other structural issues that are blocking your airway.
Here are the main types:
Nerve stimulation
This involves placing a small device inside your body. The device stimulates the nerves controlling your airway. It helps prevent blockages during sleep.
Tissue reduction
In this procedure, excess tissue in your throat is reduced or removed to clear the airway. It’s often done using radiofrequency ablation, which is minimally invasive.
Tissue removal
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) is a surgery that removes excess tissue from the back of your throat to widen your airway.
Jaw repositioning
This surgery moves your jaw forward to create more space for your airway, reducing the chance of blockages.
Tracheostomy
As a last resort for severe cases, a tracheostomy creates an opening in the neck to allow direct airflow into the windpipe, bypassing any blockages.
Adaptive Servo-Ventilation (ASV)
For individuals with central sleep apnea, adaptive servo-ventilation (ASV) is a high-tech device that continuously monitors breathing patterns and adjusts airflow to prevent pauses in breathing.
ASV is particularly effective for those whose sleep apnea is caused by irregular brain signals to the muscles that control breathing.
At QCG, we’ll help you connect best surgeons worldwide!
Sleep apnea treatment abroad
Sometimes, the best care isn’t always in your backyard. With QCG, we can connect you to top specialists around the world, giving you access to affordable, high-quality treatment for sleep apnea.
Whether it’s advanced surgeries, specialized sleep clinics, or custom treatments, you have more options than ever before. Some popular destinations for sleep apnea treatment include:
- India: Known for affordable, high-quality care, India offers advanced treatments and world-class facilities at a fraction of the cost.
- Turkey: A growing hub for medical tourism, Turkey’s hospitals offer top-notch sleep apnea surgeries and treatment options.
- Thailand: Renowned for its medical expertise, Thailand combines top medical care with a reputation for excellent hospitality.
- Mexico: Close to home for North American patients, Mexico provides high-quality treatments at much lower prices than the U.S.
Ready to explore treatment options abroad? Let QCG help you find the right care in the right place.
Say goodbye to the effects of sleep apnea!
Living with sleep apnea can make you feel exhausted every day. However, it doesn’t have to be like this. If you find yourself feeling tired during the day or notice symptoms like gasping for air at night, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional. Why keep struggling through your days when a better night’s sleep is just a step away?