Most Common Pediatric Orthopedic Surgeries Abroad: What You Need to Know
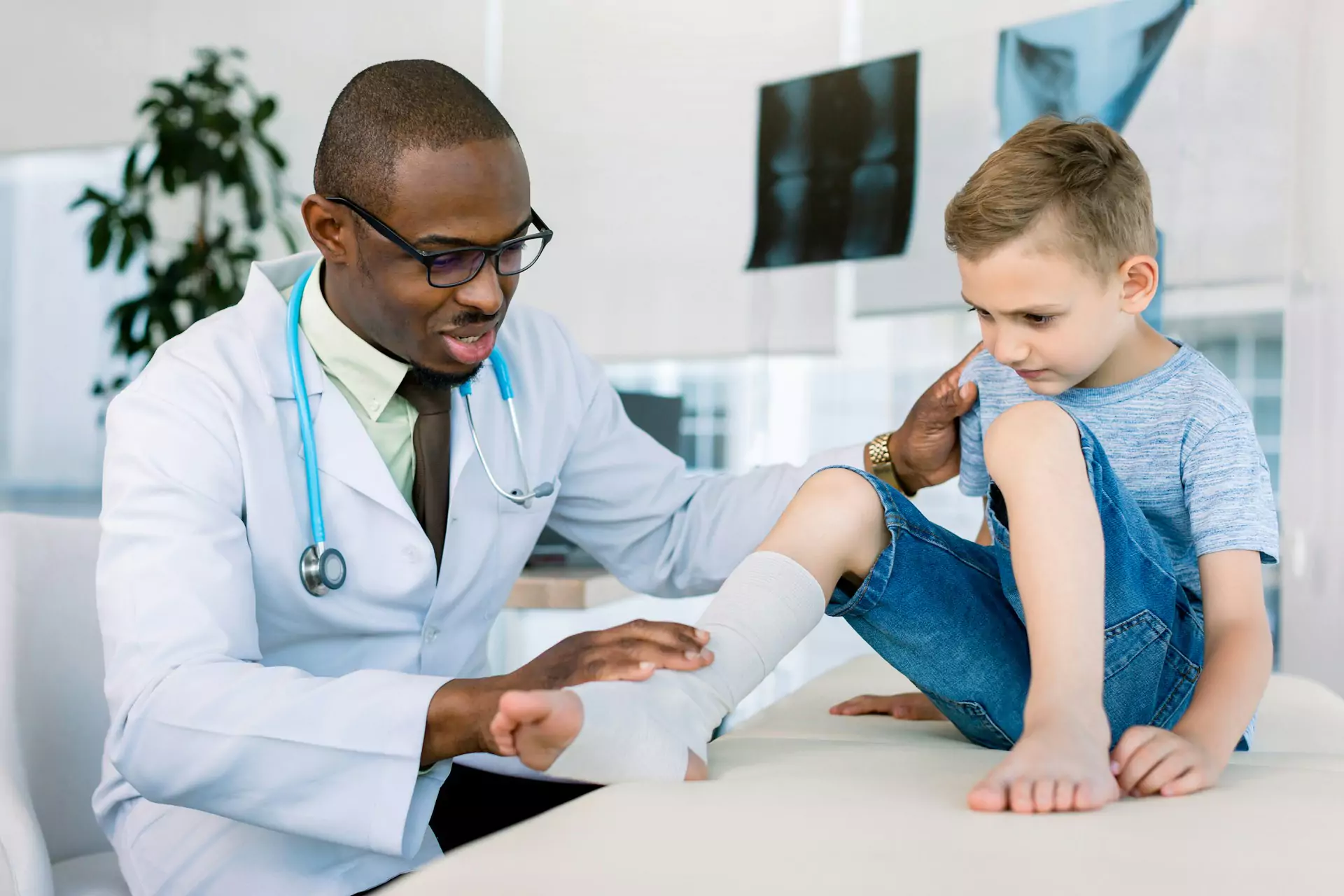
When your child experiences bone, joint, or muscle problems, it can be overwhelming. Whether it's due to a birth defect, an injury, or something else, pediatric orthopedic surgeries may be needed.
These surgeries are specifically designed to treat musculoskeletal issues in children, and they’re different from adult procedures because kids’ bones are still growing.
In this blog, we’ll walk you through some of the most common pediatric orthopedic surgeries your child might face. Let’s read on!
What is pediatric orthopedic surgery?
Pediatric orthopedic surgery focuses on conditions that affect children’s musculoskeletal systems, which include bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Children have unique needs because their bones are still growing. This is why surgeries must be planned carefully to ensure they do not interfere with their future growth and development.
Pediatric orthopedic surgeons work closely with young patients to plan and perform surgeries that help them regain full movement, reduce pain, and correct any deformities.
Some of the common conditions treated with pediatric orthopedic surgery include
-
Scoliosis (curved spine)
-
Hip dysplasia (misalignment of the hip joint)
-
Clubfoot (misalignment of the foot at birth)
-
Bone fractures
-
Limb length discrepancies (unequal limb lengths)
-
Cerebral palsy-related deformities
Which orthopedic surgeries are most common in children?
Now let’s take a closer look at the most common pediatric orthopedic surgeries and why they are performed.
Fracture fixation surgery
Kids are naturally active, which makes them more prone to fractures and broken bones. Whether it’s from playing sports, climbing, or simply running around, fractures are a common injury in childhood.
According to research, fractures account for 25% of all childhood injuries, making fracture repair surgeries one of the most frequently performed pediatric orthopedic procedures worldwide.
While many fractures can heal with the help of a cast, some need surgery to ensure the bone heals properly. Fracture fixation surgery is often performed to realign and stabilize the bone. Surgeons use metal pins, screws, or plates to hold the bone in place while it heals.
Sometimes, a cast is used along with these stabilizing devices. This ensures that the bone heals properly, preventing long-term complications such as deformities or limited movement.
The most common fractures that may need surgery to fix include:
-
Supracondylar fractures (near the elbow)
-
Femur fractures (thigh bone fractures)
After surgery, your child will typically need some time to rest and recover. Physical therapy may be needed to help rebuild strength, movement, and function in the injured limb. Most of the time, once the bone has healed, your child can get back to their usual activities. However, recovery time can vary depending on how severe the fracture was.
Scoliosis surgery
Scoliosis is one of the most common conditions treated by pediatric orthopedic surgeons. It occurs when the spine curves abnormally, either to the left or right. While some children may have mild curves that don’t cause any problems, others may develop more severe curves that can lead to pain, breathing difficulties, or even internal organ damage if left untreated.
In severe cases, surgery is necessary to prevent the curve from worsening. The most common surgical procedure for scoliosis is called spinal fusion, where the surgeon joins two or more vertebrae together to straighten the spine and prevent further curvature.
Metal rods, screws, or other devices are used to hold the spine in place while it heals. The bones in the spine then fuse together, creating a straightened spine.
A study found that posterior spinal fusion accounted for about 21% of all pediatric orthopedic surgeries.
Scoliosis surgery has a high success rate, with most children reporting pain relief and a significant improvement in posture after the procedure.
The recovery process usually involves physical therapy to help your child regain strength and flexibility. After recovery, most children can resume normal activities, including sports, with little to no long-term issues.
Hip reconstruction surgery
Hip dysplasia is when the hip joint doesn’t develop as it should. It can either be present at birth or develop as a child grows. When the hip joint isn’t properly aligned, it can lead to pain, restrict movement, and may cause arthritis later on if not treated.
There are several surgical options to treat hip dysplasia, depending on how severe the condition is.
-
One common procedure is closed reduction, a minimally invasive surgery where the surgeon repositions the hip joint without making a large incision.
-
In more severe cases, open reduction might be needed, which involves making an incision to remove tissue blocking the joint or realigning the bones to improve the fit of the joint.
-
Another procedure, called pelvic osteotomy, involves reshaping the hip socket so that the joint fits more properly.
The goal of hip reconstruction surgery is to correct the alignment of the hip joint, reduce pain, and prevent long-term issues like arthritis. With early treatment, children can avoid severe joint damage and regain normal function.
Early surgical intervention improves outcomes in 85% of hip dysplasia cases, helping children avoid future joint problems.
Recovery times vary, but most children are able to return to normal activities after a period of rehabilitation.
Clubfoot correction
Clubfoot is a condition that affects about 1 in every 1,000 babies. It occurs when one or both feet are turned inward and downward, making it difficult for the child to walk normally.
In many cases, doctors can treat clubfoot with non-surgical methods, such as casting and stretching. In most cases, the Ponseti method (a non-surgical treatment using casts) successfully corrects the condition. However, in more severe cases, surgery is needed to lengthen tight tendons and reposition foot bones for proper alignment.
Thanks to modern techniques, the success rate of clubfoot correction is very high. Most children who undergo surgery are able to walk and run normally by the time they reach preschool age.
Limb lengthening surgery
Limb length discrepancy occurs when one leg is shorter than the other. This can happen due to factors like birth defects, growth issues, or injuries that affect the growth of one limb. In cases where the difference is significant, surgery can help correct the imbalance and improve the child's ability to move.
Limb lengthening surgery involves the surgical cutting of the bone, followed by a gradual process of lengthening the bone using a device that applies tension. This device can either be external (a frame around the limb) or internal (rods implanted inside the bone). Over time, the bone gradually grows longer and fills in the gap.
Research indicates a 90% success rate for limb lengthening procedures.
The procedure can take several months, but it can significantly improve your child’s ability to walk and balance. After the bone has lengthened, your child will likely undergo physical therapy to help strengthen the muscles and regain full function. While the procedure is lengthy, the results are often life-changing, helping your child achieve better symmetry and mobility.
Osteotomy
Osteotomy is a specialized surgical procedure used to correct bone deformities by cutting and reshaping the bone. It is often performed in children with conditions such as severe bowlegs, Blount’s disease, or knock-knees, where the natural bone growth pattern has led to misalignment. Left untreated, these conditions can cause pain, difficulty walking, and long-term joint problems.
In this procedure, the surgeon removes or adds a small wedge of bone to straighten the limb and improve movement. In many cases, metal plates, screws, or rods are used to stabilize the bone while it heals. This procedure not only helps children walk with ease but also prevents future joint damage.
Since osteotomy is a major surgery, recovery takes time. Your child will likely need to use crutches, braces, or a wheelchair for several weeks to avoid putting weight on the healing bone.
Physical therapy is a key part of the recovery process, helping kids regain strength, flexibility, and balance. Most children return to their normal activities within 3 to 6 months, although full recovery can take up to a year depending on the severity of the condition.
Knee arthroscopy
Kids love to run, jump, and stay active—but with all that movement comes the risk of knee injuries. Whether it’s a torn meniscus, ligament damage, or persistent joint pain, some knee problems need more than just rest to heal properly. In these cases, surgery might be necessary.
Knee arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that allows doctors to examine and repair the knee joint without making large incisions. Using a tiny camera (arthroscope) and small surgical instruments, the surgeon can fix the issue while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues. This means less pain, smaller scars, and a faster recovery compared to traditional knee surgery.
One of the biggest advantages of this procedure is the shorter recovery time. Since it’s less invasive, kids can return to their normal activities much sooner, with minimal discomfort. Many young athletes who undergo this procedure can get back to sports with the help of physical therapy and rehab.
Ready to take the next step for your child's orthopedic care? Get in touch with QCG for a seamless and hassle-free medical journey.
What countries are best for pediatric orthopedic surgery?
If you’re considering orthopedic surgery for your child, you might wonder where the best care is available. Fortunately, there are several countries known for their excellent medical facilities and experienced surgeons in this field.
Here are a few top destinations that stand out:
1. India
India is a favored destination for families looking for affordable and high-quality pediatric orthopedic care. Hospitals like Apollo Hospitals and Fortis Healthcare provide treatment for various conditions in children, including fractures and hip issues.
2. Turkey
Turkey is known for its modern healthcare infrastructure and skilled medical professionals. With facilities like Acibadem and Memorial Healthcare Group, many international patients come here for orthopedic surgeries due to the combination of expertise and more affordable prices.
3. Germany
Germany is highly regarded for its medical precision and state-of-the-art technology. Hospitals such as Charité Berlin and Heidelberg University Hospital are well-known for offering excellent pediatric orthopedic care, making it a trusted option for families seeking the best treatment.
4. South Korea
South Korea is recognized for its advanced techniques and minimally invasive surgical procedures. Leading hospitals like Seoul National University and Asan Medical Center specialize in pediatric orthopedics, attracting patients from around the globe due to their high standards of care.
5. Mexico
For families located in North America, Mexico offers a convenient and affordable option for pediatric orthopedic surgery. Hospitals like Hospital Angeles deliver a broad range of treatments, and many doctors speak English, making it easier for international patients to navigate their care.
6. Thailand
Thailand is a popular destination for pediatric orthopedic care due to its affordable costs and skilled surgeons. Hospitals like Bumrungrad International and Bangkok Hospital offer excellent facilities and a family-friendly atmosphere.
7. Spain
Spain is renowned for high-quality healthcare and top pediatric orthopedic surgeons. Hospitals such as Hospital Sant Joan de Déu and Quirónsalud Madrid are known for their excellent care and patient comfort.
Factors to consider when choosing a country
When deciding where to go for your child’s surgery, keep these factors in mind:
-
Look for hospitals with experienced pediatric orthopedic specialists.
-
Choose hospitals accredited by international organizations like JCI.
-
Compare prices, but don’t compromise on quality.
-
Ensure the hospital staff can communicate in your preferred language.
-
Check if the hospital offers rehabilitation and follow-up services.
Preparing for the orthopedic surgery
Here’s how you can prepare for your child’s pediatric orthopedic surgery:
-
Complete all the necessary tests and medical clearances as directed by your surgeon.
-
Talk to your child about the surgery in a way they can understand, so they’re less anxious.
-
Follow the instructions on which medications to avoid before surgery, typically including anti-inflammatories like ibuprofen or aspirin.
-
Make sure to follow the fasting guidelines your surgeon gives you to ensure safety during anesthesia.
-
Bring comfortable clothing, personal toiletries, and any comfort items your child might need during their hospital stay.
Is it worth going abroad for your child’s orthopedic surgery?
Opting for pediatric orthopedic surgery abroad can be a great choice for several reasons. Many countries offer world-class medical care with highly experienced surgeons, often at more affordable prices than in your home country. Whether it’s a complex procedure or a routine surgery, international hospitals provide advanced technology and exceptional care tailored to your child’s needs.
In addition to expert treatment, international hospitals are known for their welcoming environment and family-oriented care, ensuring your child’s comfort and well-being during recovery.
If you’re exploring options for your child’s orthopedic surgery, QCG can help connect you with the right resources and guide you through the process. Contact us to learn more about international care options and find the best fit for your family’s needs.

